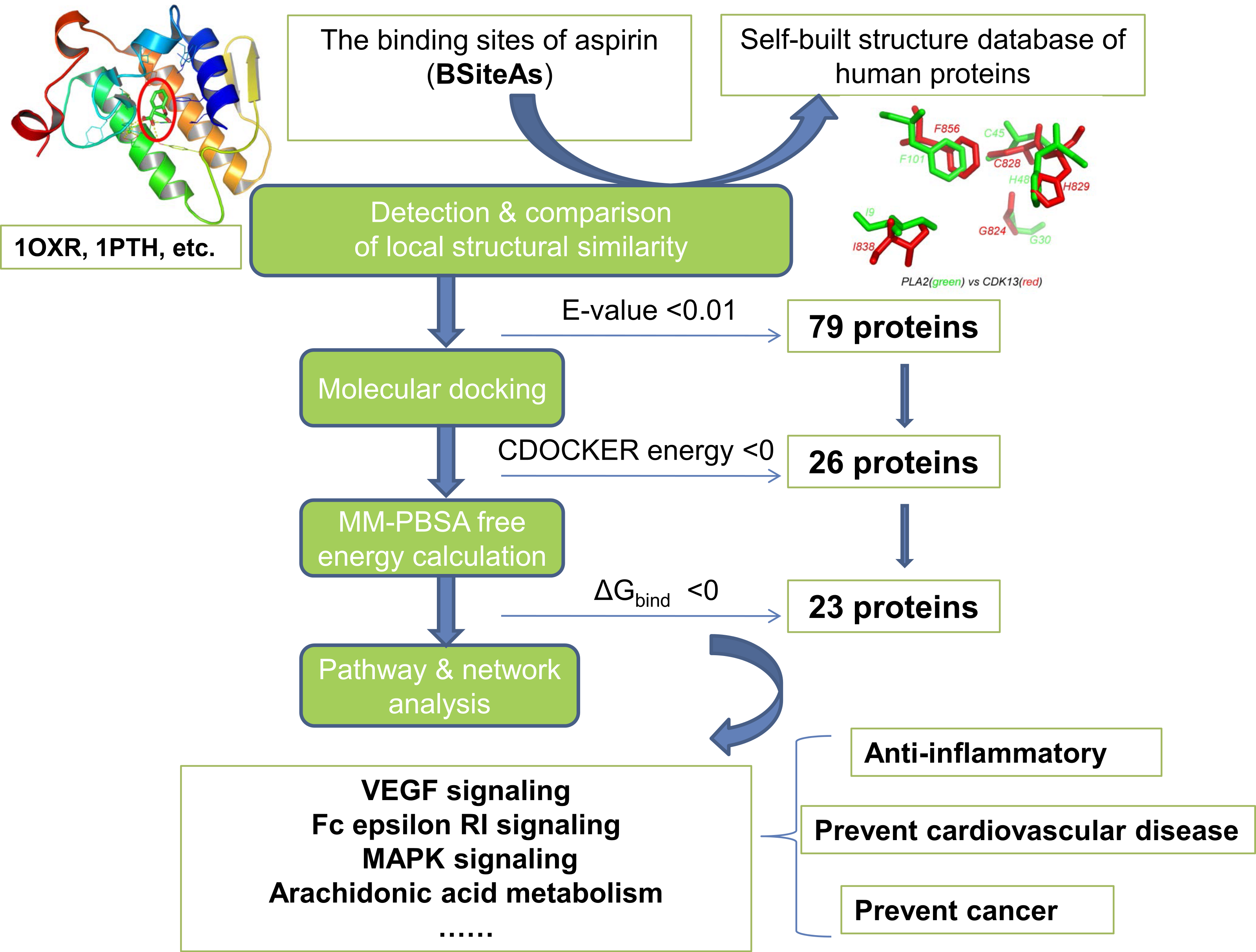
Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant . Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web open in viewer.
from ar.inspiredpencil.com
Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web open in viewer. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible.
Aspirin Mechanism Of Action
Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Web open in viewer. Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Aspirin Mechanism Of Action Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Web open in viewer. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.researchgate.net
An overview of mechanism of action of the anticoagulant drugs, showing Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web open in viewer. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.researchgate.net
Mechanism of action of aspirin and COX inhibition. Prostaglandins Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web open in viewer. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature.. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.eurekalert.org
Aspirin’s mechanism of action [IMAGE] EurekAlert! Science News Releases Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.micoope.com.gt
Asprin Mechanism Of Action Antiplatelet Activity, 54 OFF Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Aspirin Mechanism Of Action Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web open in viewer. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Web. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.researchgate.net
Action mechanism of aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitors. Aspirin irreversibly Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From basicmedicalkey.com
Anticoagulants, Antiplatelets, and Thrombolytics Basicmedical Key Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web open in viewer. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Web antithrombotic effects. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.researchgate.net
Schematic presentation of the mechanisms of how aspirin interferes with Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web open in viewer. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders,. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Aspirin Mechanism Of Action Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web open in viewer.. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Perioperative management of antiplatelet therapy in patients with Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web open in viewer. Aspirin. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.youtube.com
Aspirin Mechanism of Action AK The Pharmacist YouTube Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and.. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.pinterest.com
Image result for aspirin mechanism of action Aspirin, Cardiovascular Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web open in viewer. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders,. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.ahajournals.org
Aspirin Circulation Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Web open in viewer. Web. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Aspirin Mechanism Of Action Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and.. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Aspirin Mechanism Of Action Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Web open in viewer. Web the ability of aspirin to inhibit platelet aggregation has positioned this agent within the most frequently used drugs worldwide. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From www.micoope.com.gt
Asprin Mechanism Of Action Antiplatelet Activity, 54 OFF Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh and lmwhs (figure 1), but lmwhs have fewer side effects and. Web open in viewer. Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Noncoated aspirin acts within minutes of ingestion to stop platelets from forming blood clots. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web the ability of aspirin. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Aspirin Mechanism Of Action Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant Web antithrombotic effects of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) reported in the literature. Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible. Web open in viewer. Web anticoagulant medications are used widely for a variety of medical and surgical diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with. Web the antithrombotic action of aspirin has long been recognized. Web the principal mechanism of action is similar for ufh. Mechanism Of Action Of Aspirin As Anticoagulant.